Laparoscopic Infection Treatment: Your Ultimate Guide
In This Article
Laparoscopic Infection Treatment: Your Ultimate Guide
Sidharth
Updated on August 26, 2024
Medically verified by Dr. Arya
Fact checked by Dr. Sharon
Laparoscopic
8 min read
Laparoscopic surgery is a modern way of doing procedures through small cuts. It has many benefits, but it's important to know that infections can happen.
Our aim here is to give you clear, easy-to-understand information. We'll explain what laparoscopic surgery is, why it's better than regular surgery, and how to recognise and handle infections that might show up. By the time you finish reading, you'll have a better idea of laparoscopic infections, which will help you make smart choices about your health.
Now, let's start by learning the basics of laparoscopic surgery.
Understanding Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a modern approach to surgical procedures. Instead of one large incision, like in open surgery, your surgeon makes several small cuts. These small cuts are where they insert special instruments and a tiny camera. This camera, called a laparoscope, helps your surgeon see inside your body on a screen.
Advantages over Traditional Surgery
Why do doctors use laparoscopic surgery? Well, it has some advantages:
- Smaller incisions mean less pain
- Faster recovery for most patients
- Reduced risk of infection due to less open space
- Smaller, less noticeable scars
| Experience | Open Surgery | Laparoscopic Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Scars | Large | Small |
| Blood | Loss | MoreLess |
| Hospital Stay | 4-7 days | 1-2 days |
| Recovery | 1-2 weeks | 3-5 weeks |
Common Laparoscopic Procedures
Doctors use this technique for various procedures. Some common ones include:
- Gallbladder removal
- Appendix removal
- Colon surgeries
- Hernia repair
- Some weight loss surgeries
Your doctor will choose laparoscopic surgery when it's safe and suitable for your condition. Understanding these basics is the first step in being informed about your healthcare. Next, we'll look at what kinds of infections can occur during these procedures.
Types of Surgical Site Infections (SSIs)
Now, let's talk about the different types of surgical site infections, or SSIs for short. Even though doctors take many precautions to prevent infections during surgery, sometimes, when there's a cut in the skin, an infection can still happen. These infections are called SSIs because they occur right where the surgery was done.
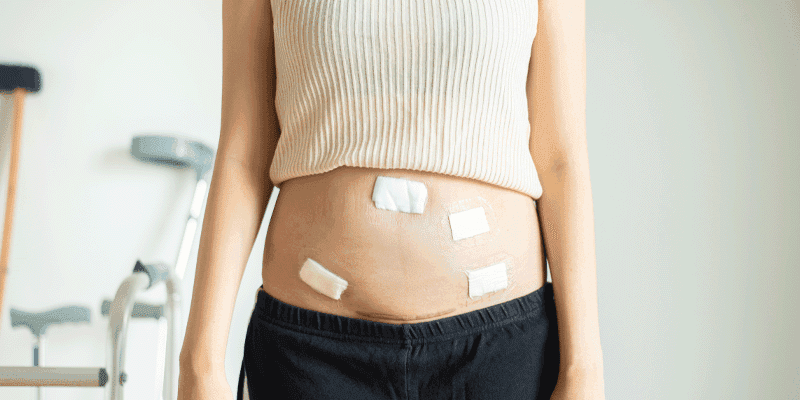
1.Superficial Incisional SSI This type of infection happens on the skin's surface right where the surgeon made the incision, the cut. It's like an infection that stays close to the surface, on your skin.
2.Deep Incisional SSI Now, this infection goes deeper beneath the incision. It can affect the muscles and the tissues around the muscles. So, it's a bit more inside your body than the superficial one.
3.Organ or Space SSI This is a more serious type. It can occur in any part of your body, not just on the skin or in the muscles. It can affect organs inside your body or the spaces between them.
Remember, while the chance of getting an SSI is small, it's essential to be aware of these types so you can spot any signs of infection after surgery.
Risk Factors for Infections
Infections after surgery are caused by tiny germs, such as bacteria. The most common culprits are Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Pseudomonas bacteria. These little germs can find their way into a surgical wound in different ways. It might be from a caregiver's touch, a surgical tool, the air, or even germs already in your body that sneak into the wound.
Types of Surgical Wounds
The type of surgical wound you have can affect the risk of getting an SSI:
1.Clean Wounds These wounds are not inflamed or contaminated and don't involve operating on an internal organ. They have the lowest risk.
2.Clean-Contaminated Wounds These wounds have no sign of infection when surgery starts, but they do involve operating on an internal organ. The risk is a bit higher than clean wounds.
3.Contaminated Wounds These wounds involve operating on an internal organ with some spilling of organ contents into the wound. It's riskier than the clean types.
4.Dirty Wounds These wounds have a known infection at the time of surgery. They have the highest risk.
 9 min read
9 min readTop 9 Things To Know About Laparoscopic Treatment for Pregnancy
 9 min read
9 min readHow Much Does Laparoscopy Treatment Cost? Here's The Truth
 8 min read
8 min readTreatment After Laparoscopy for Pregnancy - What You Need to Know
Get a Callback Now
Other Risk Factors for SSIs
In addition to the type of wound, several other things can increase the risk of SSIs. These include:
- Having surgery that lasts more than 2 hours
- Having other medical problems or diseases
- Being an elderly adult
- Being overweight
- Smoking
- Having cancer
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having diabetes
- Undergoing emergency surgery
- Having abdominal surgery
While these factors can increase the risk, many surgeries are successful without any infections. Your healthcare team will take steps to minimise these risks and ensure your safety during and after surgery.
Recognizing Infection Symptoms
Common symptoms of an SSI after surgery include:
1.Redness and Swelling Pay attention to the area around your surgical incision. If it becomes red and starts to swell, that's a sign you should take seriously.
2.Drainage of Pus If you notice any yellow or cloudy pus coming from the incision site, it's a clear indicator of a possible infection.
3.High Fever A fever, especially one that spikes to about 100.3°F (38°C) or higher for more than 24 hours, can also be a symptom of an SSI.
Preventing Infections
There are important steps you can take to help prevent infections before and after surgery:
Before Surgery
1.Use an Antiseptic Cleanser Your doctor may provide you with a special antiseptic cleanser to use before going to the hospital. This helps reduce the number of germs on your skin, lowering the risk of infection.
2.Skip Shaving Avoid shaving the surgical area before your operation. Shaving can irritate your skin and introduce germs beneath the surface.
3.Quit Smoking If you smoke, consider quitting before your surgery. Smokers are more susceptible to infections.
After Your Surgery
`1.Maintain Your Dressing Keep the sterile dressing applied by your surgeon on your wound for at least 48 hours. This dressing protects your incision from germs.
2.Take Preventive Antibiotics If prescribed, ensure you take preventive antibiotics as directed. They can further reduce the risk of infection.
3.Wound Care Understand how to care for your wound, and don't hesitate to seek clarification if needed.
4.Hand Hygiene Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before touching your wound. It's crucial, and anyone assisting with your care should do the same.
5.Be Proactive Pay attention to your surroundings in the hospital. Observe how often your wound is being dressed, ensure your room is clean and sterilised.
By taking these steps, you actively contribute to minimising the risk of infection. Your healthcare team is here to support you at every stage, so if you have any questions or concerns, do not hesitate to reach out. Your well-being is our top priority.
What Happens When Infections Are Left Untreated
When it comes to laparoscopic infections, it's important to understand what might happen if they're not treated:
1.Spread and Severity It could spread to other parts of your body, making you feel worse and needing more treatment.
2.Abscess Formation Sometimes, untreated infections can create pockets of pus called abscesses. These might require more procedures and take longer for you to recover.
3.Delayed Healing Infections that stick around can slow down the healing of your wound. This might leave bigger scars and make you uncomfortable for a longer time.
Treatment Approaches for Laparoscopic Infections
Healthcare providers use a combination of methods when it comes to treating infections:
1.Antibiotics and Medications
Antibiotics are commonly used to treat most surgical wound infections. If you have an infection, your doctor will likely start you on antibiotics. The duration of your antibiotic treatment can vary but often lasts for at least a week.
Initially, you may receive antibiotics through an IV, but later, you might switch to taking pills. It's crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better.
In cases where there is drainage from your wound, the fluid may be tested to identify the most effective antibiotic.
2.Surgical Procedure Occasionally, your surgeon may need to perform a procedure to clean the wound. This can be done in the operating room, your hospital room, or a clinic setting. During this procedure, your surgeon will:
1.Open the wound by removing some or all of the staples or sutures.
2.Conduct tests on the pus or tissue from the wound. This helps determine the type of infection and which antibiotic would be most effective.
3.Remove any dead or infected tissue within the wound (a process called debridement).
4.Rinse the wound with a saline solution (saltwater).
5.Drain any pockets of pus (abscesses) if present.
6.Pack the wound with dressings soaked in saline and cover it with a bandage.
Risks with Different Treatments
1.Antibiotics They are usually safe, but they can sometimes cause stomach issues or allergic reactions. If you ever feel strange while taking antibiotics, tell us.
2.Surgical Procedures There are risks like bleeding, more scars, or complications from anaesthesia when surgery is done to treat deeper infections.
The choice of treatment depends on the type and how bad the infection is. Sometimes, we need surgery along with antibiotics to clear the infection.
Laparoscopic Surgery: It's a modern method using small cuts and a camera. It means smaller scars, less pain, and a quicker recovery.
Infection Types: Infections can happen, even with care. There are three types: on the skin, deeper inside, and in the body spaces.
Infection Risks: Tiny germs like bacteria cause these infections. Factors like wound type, surgery length, and health conditions affect risk.
Recognise Infections: Look for signs like redness, swelling, pus, or a fever after surgery. Tell your doctor if you notice these.
Prevent Infections: Follow instructions before surgery, keep your wound clean, take antibiotics as told, and wash your hands.
Complications and Risks: Untreated infections can lead to worse problems. Treatment has some risks, but your team will be careful.
Treatment Approaches: Usually, we use antibiotics. Sometimes, surgery is needed for serious infections.
Antibiotic Safety: Antibiotics are usually okay but can upset your stomach or cause allergies. Finish all the medicine even if you feel better.
Surgery Risks: Surgery has its own risks, like bleeding or more scars. We pick the treatment based on how bad the infection is.



