Gynecomastia vs. Fat: How to Tell the Difference
In This Article
Gynecomastia vs. Fat: How to Tell the Difference
Nimisha
Updated on October 04, 2024
Medically verified by Dr. Arya
Fact checked by Dr. Fazeela

Cosmetic
5 min read
Most men suffer from enlarged breast tissue also known as ‘man boobs’.
It is also known as gynecomastia which is a result of hormonal imbalances that prompt the development of glandular breast tissue.
Sometimes this can just be fat as a result of weight gain.
Differentiating between these conditions is very important so as to ensure proper management.
This guide by Mykare Health examines the possible causes of gynecomastia and the possible diagnosis to make of pseudogynecomastia including the main symptoms and the available treatments.
Understanding Gynecomastia
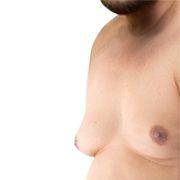
Gynecomastia is male breast enlargement which is attributed to an oestrogen testosterone disparity.
This may occur in either breast or both affecting one’s breast leading to classic presentation of lobulated, irregular, firm to rubbery lump beneath the nipple.
It can affect anybody at any age but it is more prevalent during puberty, middle aged adults, as well as the older adulthood age bracket.
Causes of Gynecomastia
-
Hormonal Imbalance: This may be due to a high level of oestrogen, or a low level of testosterone, and results in the fleshy formation of growth in the breast.
-
Medications: Anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, antidepressants, and cardiac solutions are some of the drugs that are associated with gynecomastia.
-
Health Conditions: Pathology can alter levels of hormones; primary examples are hyperthyroidism, kidney or liver disease and tumour.
-
Substance Use: Drugs such as Alcohol, Marijuana and other Recreational Drugs do have an impact on hormonal balance and can cause Gynecomastia.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
-
Mammographic visibility of hard, round mass, irregular or smooth of border lying immediately beneath the nipple areola complex.
-
Nipple or breast pain/tingling.
-
May occur on one or both breasts, which may be different in size and shape.
Understanding Pseudogynecomastia (Fat Accumulation)
Lipomastia or pseudogynecomastia is defined as enlarged fatty breasts without growth of glandular tissues. Which is quite common in the overweight and the obese and it arises from the general obesity rather than the hormonal one.
Causes of Pseudogynecomastia
-
Obesity: Increased energy consumption and decreased energy expenditure result in general obesity and the deposit of fat in the chest cavity.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: It is a fact that when people fail to exercise, fat deposits are made on the body and muscles become flabby.
-
Diet: Consumption of highly processed foods, sugars as well as unhealthy fats results in fat deposition in various regions of the body including the chest region.
Symptoms of Pseudogynecomastia
-
Flabby, non fatty tissue without a hard glandular nodule.
-
Can be done without any pain or any sensitivity felt in the affected area.
-
The fattening is proportional to the overall increase in the weight of the body.
 9 min read
9 min readThe Advantages of Choosing Mykare Health for Gynecomastia Surgery
 6 min read
6 min readIdentifying The Ideal Age For Gynecomastia Surgery
 6 min read
6 min readPre and Post Gynecomastia Surgery: Essential Things to Know
Get a Callback Now
Gynecomastia and Pseudogynecomastia
There is a difference between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia and it is crucial to make the differentiation since the management of the two conditions varies slightly.
This can be made through physical examination, imaging and sometimes blood tests.
1. Physical Examination
-
Gynecomastia: Tympanic and well-defined, a firm, rubbery mass can be felt directly under the nipple.
-
Pseudogynecomastia: The chest feels less tight, and the fat is distributed more evenly and no firm mass can be palpated; pinching it away from the glandular tissue is helpful; in gynecomastia, there is still a firm disk-like feel.
2. Diagnostic Imaging
-
Ultrasound: Is useful in differentiation between fatty tissue and glandular tissue; gynecomastia is glandular while pseudogynecomastia is fat.
-
Mammography: If there is doubt of breast cancer or in an attempt to establish the kind of breast tissue.
3. Blood Tests
- Screen the patient with blood tests to check hormonal levels such as testosterone, oestrogen, among others if hormonal disbalance is the cause of gynecomastia.
Treatment Options
For Gynecomastia
-
Observation: Mild forms of the condition especially during puberty may subside on their own.
-
Medications: Agents like tamoxifen or raloxifene can be used in order to balance the levels of hormones present into the body.
-
Surgery: In cases where the condition is chronic or severe liposuction or in the case of the breast; mastectomy is used to excise the glandular tissue.
For Pseudogynecomastia
-
Weight Loss: The principal treatments include dieting and physical exercise with the aim at achieving general weight loss.
-
Strength Training: Men can also benefit from chest exercises resistance exercises in that they help in development of chest muscles.
-
Liposuction: Discuss if fat does not decrease enough when one decides to shed off some weight.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage and prevent both conditions:
-
Diet: Weight maintenance in general is achieved when taking food of proper proportions and avoiding foods with high sugar content and those that have undergone through processing.
-
Exercise: Cardiovascular activities which include jogging, cycling etc and strength training when done regularly assist in burning body fat and building muscles respectively.
-
Avoiding Substances: Alcohol, recreational drugs and carefully monitored medications are some of the strategies that help in avoiding hormone interferences.
To decide the right therapy, it is important to distinguish between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia.
Gynecomastia has some causes associated with hormonal imbalances and thus one may need medical or surgical attention, pseudogynecomastia on the other hand is basically fat accumulation and can easily be treated through change of diet and exercise.
Appropriate diagnosis through physical examination, imaging, and hormonal assay allows providing directed therapy, which in turn has a positive impact on clinical prognosis and patients’ quality of life.
This would be the first line of management to take if you notice changes in the chest area you should see a doctor.
Gynecomastia: Endocrine disorder leads to formation of fibrosis under the nipple; signs include breast pain and nipple pain; a physical exam, imaging, and hormonal assays diagnose; observed, medicated, or surgically treated.
Pseudogynecomastia: Caused by obesity; soft, non-tender fat; diagnosed through examination and imaging; weight loss, regular exercise, or liposuction.
Differentiation: Gynecomastia has a firm mass; pseudogynecomastia is diffuse fat; imaging and tests confirm it.
Prevention: Diet, exercise, and refraining from alcohol/drugs both eradicate possibilities of both these types of conditions.



