Is Gynecomastia Common in Teenagers?
In This Article
Is Gynecomastia Common in Teenagers?
Prathibha
Updated on February 21, 2025
Medically verified by Dr. Arya
Fact checked by Dr. Fazeela

Cosmetic
4 min read
At the onset of puberty, boys experience several physical changes, and one of the most concerning among them is gynecomastia—the enlargement of male breast tissue. This condition, often mistaken for chest fat deposition, affects a significant percentage of teenagers due to hormonal fluctuations. While it usually resolves on its own, some cases require medical intervention.
If you are a teen struggling with gynecomastia during puberty or a parent looking for solutions, this guide of Kareline will help you understand its causes, self-care tips, and treatment options.
What is Gynecomastia?
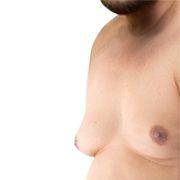
Gynecomastia is the abnormal growth of glandular breast tissue in males, leading to a more prominent chest appearance. It differs from pseudogynecomastia, which results from excess fat rather than glandular tissue. While boys with boobs may feel self-conscious, it is crucial to understand that this is a temporary and natural occurrence for most teens.
Common Symptoms
-
Swollen or tender male nipples
-
Uneven or symmetrical breast tissue growth
-
A firm lump under the nipple area
-
Emotional distress due to chest appearance
Causes of Gynecomastia in Teenagers
1. Hormonal Imbalances
The primary cause of teenage gynecomastia is an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen during puberty. Temporary surges in estrogen can lead to breast tissue development.
2. Obesity & Chest Fat Deposition
Being overweight increases estrogen production, leading to perfect teen boobs in some cases. Weight loss and exercise can help if fat accumulation is the primary cause.
3. Medications & Supplements
Certain drugs like antidepressants, steroids, and hormone treatments can trigger gynecomastia by altering hormone levels.
4. Substance Use
Alcohol, marijuana, and anabolic steroids have been linked to gynecomastia due to their effects on hormonal balance.
5.Genetic Factors & Medical Conditions
Some boys have a genetic predisposition, while conditions like thyroid disorders and liver disease may also contribute.
 9 min read
9 min readThe Advantages of Choosing Mykare Health for Gynecomastia Surgery
 6 min read
6 min readIdentifying The Ideal Age For Gynecomastia Surgery
 6 min read
6 min readPre and Post Gynecomastia Surgery: Essential Things to Know
Get a Callback Now
Gynecomastia Self-Care & Treatment Options
1. Gynecomastia Self-Care & Non-Surgical Remedies
While gynecomastia is often temporary, here are some self-care measures to manage symptoms
-
Healthy Diet & Exercise: Engage in chest-targeted workouts and reduce processed foods to balance hormone levels.
-
Wearing Compression Garments: Special chest compression vests can help conceal enlarged breasts.
-
Avoiding Triggers: Reduce alcohol, steroids, and drugs that may worsen hormonal imbalance.
2. Medical Treatment for Gynecomastia
For persistent cases, doctors may recommend
-
Hormonal Therapy: Medications like SERMs (Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators) or aromatase inhibitors help block estrogen’s effects.
-
Counseling & Emotional Support: Many teens struggle with body image issues, so professional counseling can be beneficial.
3. Gynecomastia Surgery (Teen Breast Reduction)
When gynecomastia does not resolve on its own, gynecomastia surgery (male breast reduction) is an effective solution. The two primary surgical options are
-
Liposuction: Removes excess chest fat deposition but does not affect glandular tissue.
-
Mastectomy: A cosmetic surgeon removes excess glandular tissue for a flatter chest appearance.
Where to Get Gynecomastia Treatment in Chennai?
If you're looking for a gynecomastia specialist in Chennai, Mykare Health offers safe and affordable gynecomastia surgery at some of the best hospitals in Chennai
-
Sri Srinivasa Hospital – Known for advanced gynecomastia treatment and surgical expertise.
-
Imax Hospital – Equipped with top cosmetic surgeons specializing in male breast reduction.
-
MMS Hospital – Offers comprehensive gynecomastia surgery with state-of-the-art facilities.
Final Thoughts
Teenage gynecomastia is a common yet often misunderstood condition. While most cases resolve naturally, persistent cases can cause distress. Understanding self-care strategies, medical treatments, and surgical options can help teens navigate this condition with confidence.
Looking for expert guidance? Mykare Health is here to help you find the best gynecomastia specialists in Chennai for safe and effective treatment.
Teenage gynecomastia during puberty is a common condition caused by hormonal changes.
It often resolves on its own within six months to two years as hormone levels stabilize.
Causes include hormonal imbalances, medications, substance use, obesity, genetics, and underlying medical conditions.
Pseudogynecomastia is different from true gynecomastia, as it results from chest fat deposition rather than glandular tissue growth.
Self-care measures like maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding substances that impact hormones can help manage symptoms.
Treatment options range from observation and reassurance to medication or surgery in persistent or severe cases.
Emotional and psychological support is essential, as teenage boobs can impact self-esteem and confidence.
Mykare Health offers gynecomastia treatment in Chennai at Sri Srinivasa Hospital, Imax Hospital, and MMS Hospital with expert cosmetic surgeons.
Source Links
Gynecomastia Teens - Kids health
Gynecomastia in Adolscent Male - NCBI
Teenage Gynecomastia: Banner health



