Gynecomastia in Teens: Surgery or Not?
In This Article
Gynecomastia in Teens: Surgery or Not?
Prathibha
Updated on February 20, 2025
Medically verified by Dr. Arya
Fact checked by Dr. Fazeela

Cosmetic
3 min read
Gynecomastia is a condition that leads to the enlargement of breast tissue in males, often caused by a hormonal imbalance between estrogen and testosterone. While it is common during puberty, it can be distressing for teenagers, affecting their confidence and social life. One of the biggest questions for teens and their parents is whether gynecomastia surgery is necessary or if non-surgical options can help. In this Kareline blog, you will gain valuable insights into gynecomastia solutions and learn when to seek the right treatment from professional gynecomastia surgeons.
Mykare Health provides expert consultation and gynecomastia treatment in Chennai, Bangalore, and Kochi, helping teens make informed decisions about their condition.
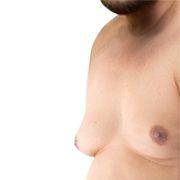
Understanding Gynecomastia Stages
Gynecomastia progresses through different stages
1. Stage 1 (Mild) – Small breast enlargement without excess skin.
2. Stage 2 (Moderate) – Moderate breast enlargement with minimal excess skin.
3. Stage 3 (Severe) – More pronounced enlargement with excess skin.
4. Stage 4 (Extreme) – Significant breast enlargement with a noticeable feminine appearance.
When Should Teens Seek Treatment?
Many teenage boys experience some degree of gynecomastia, which often resolves within 6 months to 2 years. However, treatment may be necessary if
-
The condition persists beyond two years.
-
There is significant emotional distress or embarrassment.
-
Pain or tenderness is present.
-
Underlying medical conditions contribute to gynecomastia.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Before opting for surgery, doctors recommend trying non-surgical treatments:
-
Weight Management: Losing excess weight can help reduce chest fat but does not eliminate glandular tissue.
-
Hormonal Therapy: If gynecomastia is due to hormonal imbalance, medications like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) may help.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding alcohol, marijuana, and certain medications can prevent further enlargement.
-
Dietary Adjustments: Following a gynecomastia food avoid list, such as reducing processed foods and soy-based products, may help regulate hormone levels.
 9 min read
9 min readThe Advantages of Choosing Mykare Health for Gynecomastia Surgery
 6 min read
6 min readIdentifying The Ideal Age For Gynecomastia Surgery
 6 min read
6 min readPre and Post Gynecomastia Surgery: Essential Things to Know
Get a Callback Now
When is Surgery the Right Option?
Surgery is considered when gynecomastia does not resolve with non-surgical treatments or causes significant distress. The two primary surgical options are
Liposuction: Removes excess fat but does not address glandular breast tissue.
Mastectomy: Removes glandular tissue, often combined with liposuction for the best results.
Is Gynecomastia Surgery Safe?
Yes, gynecomastia surgery is a safe procedure when performed by qualified cosmetic surgeons. However, like any surgery, there are risks, including
-
Infection
-
Scarring
-
Uneven chest contour (chest not flat after gyno surgery)
Mykare Health connects patients with gynecomastia specialists in Chennai, Bangalore, and Kochi for safe and effective treatment.
Gynecomastia Surgery Procedure & Recovery Time
The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and takes 1-2 hours. Gyno surgery recovery time varies, but most patients return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks.
Post-Surgery Care
-
Wear a compression garment for support.
-
Avoid heavy lifting for at least 4 weeks.
-
Maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine to prevent fat accumulation.
Consultation with a Doctor
If your teen is considering surgery, consulting a cosmetic surgeon is crucial. The doctor will assess
-
The severity of gynecomastia
-
Overall health condition
-
The best treatment approach (surgical or non-surgical)
For professional guidance on gynecomastia treatment, schedule a consultation with Mykare Health today!
Gynecomastia is common in teens and often resolves naturally.
Non-surgical options, including weight management and hormone therapy, should be explored first.
Surgery is an effective solution when gynecomastia persists and affects confidence.
Gynecomastia surgery recovery time is usually short, with proper post-operative care.
Mykare Health provides access to expert gynecomastia specialists in Chennai, Bangalore, and Kochi.
Source Links
TeensHealth - Gynecomastia
NIH - Gynecomastia in Adolescent Males
Gynecomastia in adolescent males: current understanding of its etiology - Apem



